PHP is the programming language behind major web applications like WordPress (blog), Drupal (CMS), and Magento (e-commerce). It first appeared in 1995, less than 3 weeks after the Java programming language.
It remains one of the top 10 programming languages in the world, according to many lists, and is the "P" in the famous LAMP stack (Linux, Apache, MySQL, and PHP).
In this tutorial, let's create a simple API using one of PHP's most popular frameworks, Laravel, and then access it with Postman.
Prerequisites
- A basic familiarity with the PHP programming language.
- Ability to use the built-in terminal in your operating system.
What You'll Learn
- How to create a simple PHP-based API with the Laravel framework.
- How to create GET and POST API endpoints for it.
- How to send requests to those endpoints with Postman.
What You'll Need
- Git Installed (Required)
- PHP Installed (Required)
- Composer Installed (Required)
- Homebrew Installed (only for Mac)
- VSCode Installed (Optional)
- Or a code editor of your choice
You will not need Apache or Nginx for this guide as we'll use PHP's built-in serving functions.
What You'll Build
- A simple API with PHP and Laravel
Let's get started in the next step.
Installing PHP
The methods below install PHP with all the module dependencies for running Laravel locally. If you have already installed PHP locally, ensure you have the modules in the Laravel server requirements installed and enabled.
MacOS
PHP is most easily installed with Homebrew.
brew install php
After installation, confirm PHP is installed with php -v in the terminal.
Windows
The basic installation of PHP on Windows from the installer provided by the PHP project lacks module dependencies Laravel requires.
The PHP 8.2 version of XAMPP installs a version of PHP with the necessary dependencies. It will also install the Apache web server, MYSQL, and other software you don't necessarily need, but it isolates all of it in a unique directory so they're easy to remove.
- Download XAMPP for your architecture. The version with PHP 8.2 (or later) is recommended.
- Install it. It will warn against installing it to your regular program files location. That's fine. When it suggests
C:\xamppas an installation directory, accept it. - Accept the default set of items being installed or deselect options you don't need (like Filezilla and Tomcat).
- When it's complete, open a terminal/command window and issue the command:
setx PATH "%PATH%;C:\xampp\php". This adds your PHP executable to your path and makes it easy to call from the command line. - Close the terminal/command window and open a new one to start a session with the updated path information.
- Test your installation with
php -vand you should get some information on the version of PHP you installed.
This was tested and worked with Windows 11 on both X86-64 and ARM architectures in March 2023.
Linux
Using the default installation of PHP may create dependency issues when you try to start a Laravel project. We suggest the following:
- Download XAMPP for your Linux distribution and Intel/AMD architecture. At the time of writing, XAMPP doesn't support Linux on ARM.
- Follow the directions to install it for your Linux distribution.
- By default on Ubuntu, it will install to the
/opt/lampp/folder. Open the~/.bashrcfile in your favorite text editor, add the following line to the end of the file, and save:
EXPORT PATH="/opt/lampp/bin:$PATH"
- Open a new terminal for a session using the updated
.bashrc. In that terminal tryphp -vto ensure it is installed and is in your path.
This was tested and worked with Ubuntu 22.04 LTS in March 2023.
Installing Composer
The Composer download and installation instructions are a little dense. Let's simplify them.
MacOS
Homebrew makes it simple.
brew install composer
If you don't have Homebrew, get it or use the Linux instructions below.
Windows
Use the Composer installer for Windows. This will automatically put Composer in your path as well, so it will be accessible from the command line.
Linux
Use the Composer installation instructions for Linux/Unix.
IMPORTANT follow the step on that page to move the installed copy into a directory that's already in your path so it's easy to call from the terminal.
Verifying Composer
Open a new terminal or command prompt and type composer -h.
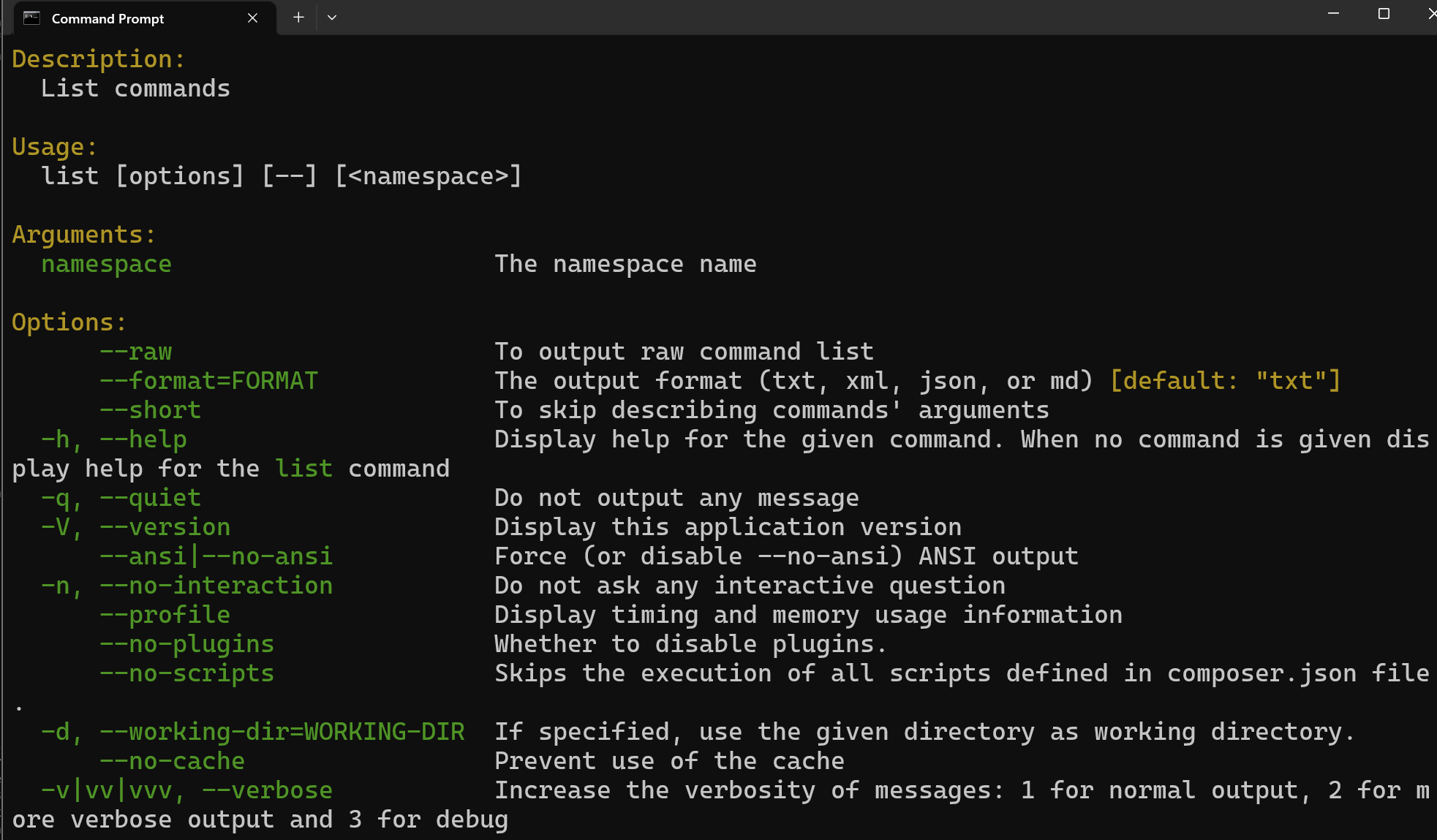
If you get an error or nothing, check your installation.
Once this is complete, let's scaffold a Laravel project.
Scaffold your Laravel project
Before we can write any code, we need to scaffold a Laravel project. Thanks to Composer, this is relatively simple. Open a terminal and navigate to the directory where this project will live. Enter the following command in the terminal:
composer create-project laravel/laravel laravel_project
This could take some time. There are tens of megabytes to download and install.
When it's finished, you will have a project folder named laravel_project.
Give it a test
Navigate into the laravel_project folder and enter the following command in the terminal:
php artisan serve --port=8080
This will launch your project at http://localhost:8080. Change the port to something else if you already have a process using the port. When it's running, visit the URL. It will return this homepage.
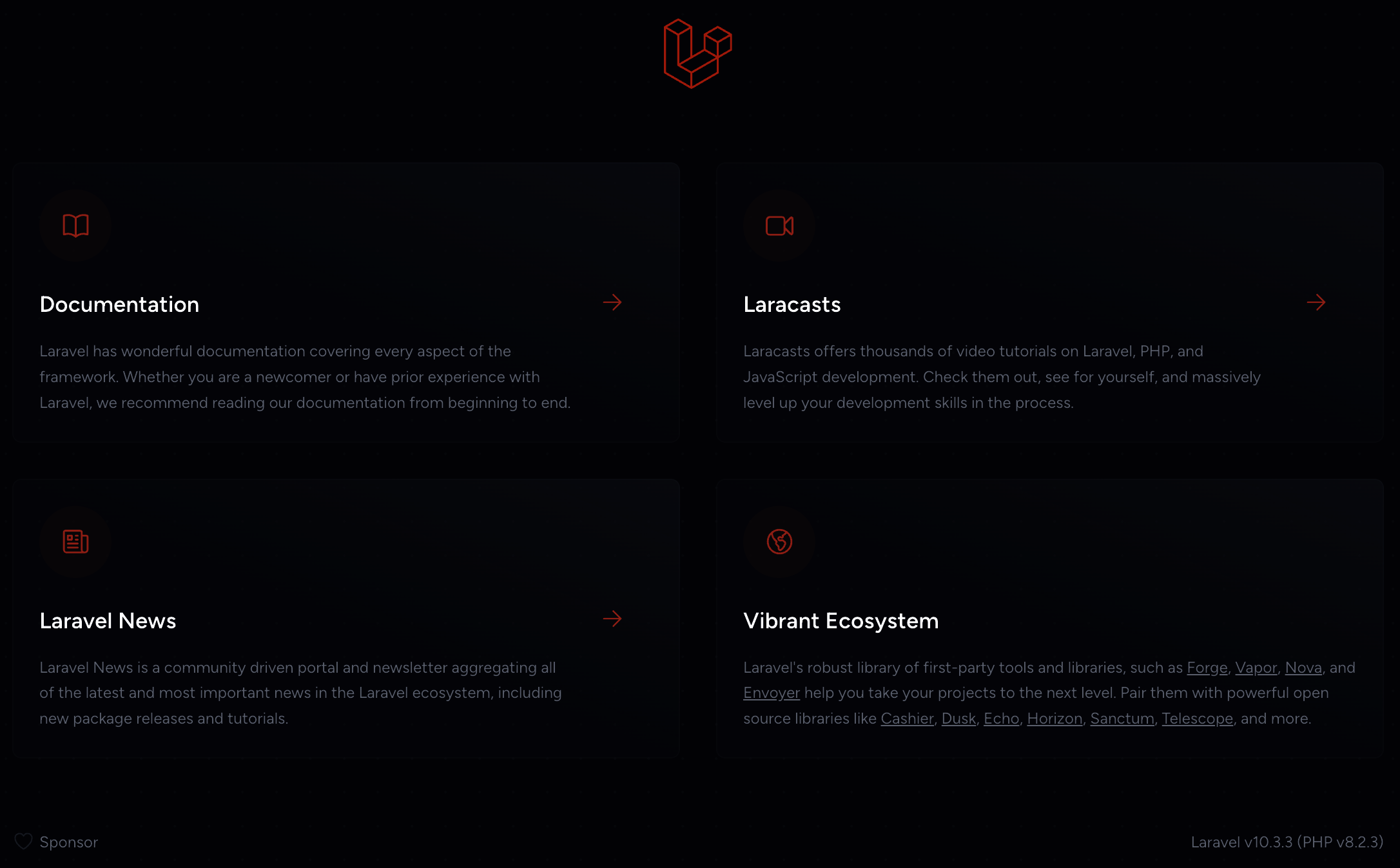
Note down in the bottom right, you'll see the Laravel and PHP version numbers. If you're looking for tutorials, finding ones for Laravel and PHP that are as close to those versions as possible will help minimize problems.
Let's move on to adding an API.
Create the route
This will create a public API with no authentication.
Open routes/api.php in your Laravel project directory in your editor. Add the following code at the end:
Route::get('/hello', function () {
return "Hello World!";
});
This adds the /api/hello endpoint and returns "Hello World" in plain text to a GET request.
Note how the endpoint was prefixed with /api by Laravel.
Next, let's call this endpoint in Postman.
To test this in Postman, open your personal workspace and start a collection. Name it Laravel QuickStart or something else you prefer.
Once it's created, select Add a request to get started.
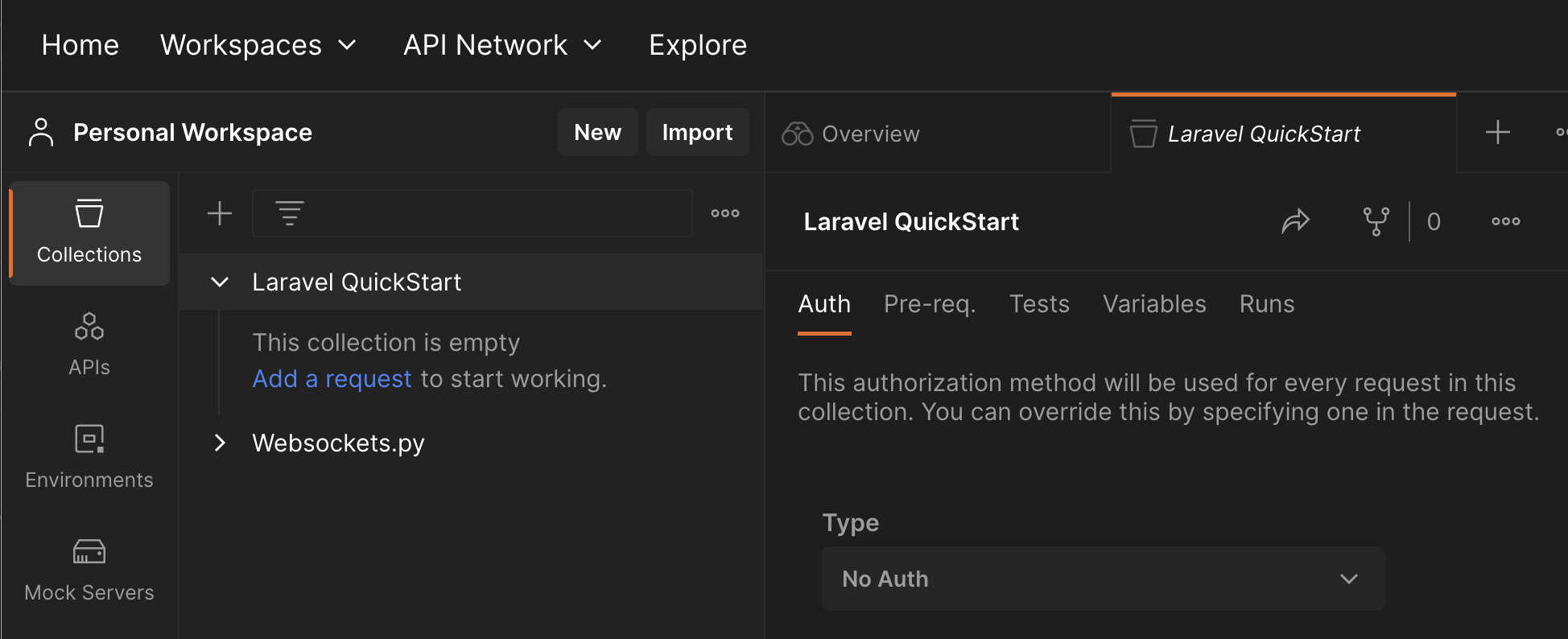
Set the request URL to localhost:8080/api/hello and make sure your Postman Desktop Agent app is running on your machine to prevent any CORS issues while testing locally.
Select Send and the response section below the request section will show a response of Hello World! in plain text with a 200 OK response code.
Congratulations. You created your first API endpoint in Laravel and successfully called it with Postman.
Next, let's make a simple POST endpoint for fun.
Go back to your routes/api.php file and add the following:
Route::post('/reverse-me', function (Request $request) {
$reversed = strrev($request->input('reverse_this'));
return $reversed;
});
This adds a POST route for the endpoint api/reverse-me. It will reverse a string you pass in the body of the post with the parameter name reverse_this.
Let's try this in the next section.
Return to your Laravel QuickStart collection in Postman and add a request. Name it "Reverse" and follow these steps:
- Set the request type to POST.
- Set the endpoint to
localhost:8080/api/reverse-me. - Select the Body tab.
- In the top dropdown menu in the tab, select x-www-form-urlencoded.
- Add a parameter of
reverse_thiswith the value ofesrever. That's "reverse" already reversed so the return value will be easy to read. - Select Send
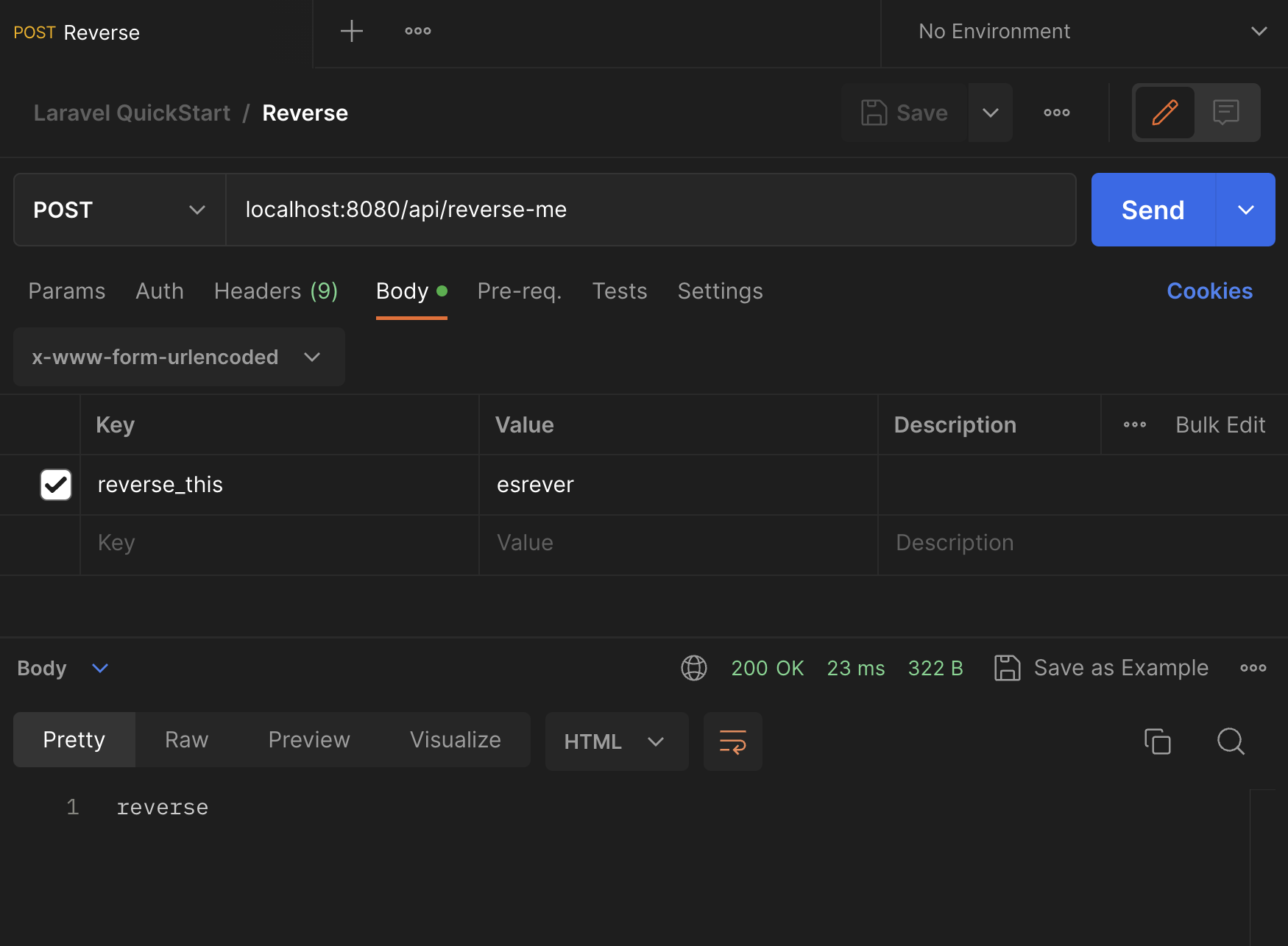
The API will return the string reverse in plain text.
Congratulations on creating an API in Laravel and accessing it with Postman.
You can deepen your knowledge of Laravel or Postman by trying the following.
- Dive into the Laravel 10.x documentation to add a controller for handling more complex requests and/or add a model to connect a database.
- Review the Laravel 10.x error handling documentation to learn best practices for error-handling in Laravel, such as what might happen if someone submitted a binary file instead of a string to your string-reversing endpoint.
- Explore the Postman testing documentation and write a test on the POST request to make sure the
reverse_thisstring is being reversed properly.